Accounting is the process of assigning a value to a company’s assets, and inventory valuation is a part of that process. It is essential to establish a reliable method for determining the value of a company’s inventory because this asset makes up a significant proportion of the total assets held by any business that deals in the sale of tangible goods.
A thorough comprehension of inventory valuation is a necessary step toward achieving maximum profitability. This not only ensures that the company can accurately report the worth of its inventory on its financial accounts, but it also assures that it can do so accurately.
Material Valuation is part of Materials Management (MM).
This includes the following application areas:
- Purchasing
- Inventory Management
- Logistics Invoice Verification
The stock value of a material is either calculated or recorded via the material valuation process.
Stock value = stock quantity x material price ( material Ledger )
Material Valuation serves the following purposes:
- Adjusting material prices to market prices or landing costs of the material as per actual invoice.
- Inventory price revaluations.
- Inventory valuation – Accounted at the Balance sheet.
- Purchase offsetting account – Accounted at the P&L sheet.
- Inventory Ageing – Based on the Purchase date ( date of goods receipt -GR or consumptions at the time of movement of goods.
- Valuation directly affects its cost of goods sold (COGS).
- Inventory valuation affects the profitability and gross income.
- Company’s financial position and Liquidity Analysis.
- Impact on Income Taxes and Statutory Compliance ( Disclose the valuation of each class of inventory).
- Impact of cost of the inventory and Net Realizable Value.
When discussing valuation, it is important to address the following questions?
- At which level are materials and type of material need to be valuated?
- Which types of goods movements are relevant for valuation?
- Which accounts must be posted to during a transaction?
- Whether a particular material should be valuated or not?
- Whether different sub-stocks of material should be valuated differently or the same level of upper level?
- Whether the stock of material should be valuated (V) moving average price or standard price (S) if yes how?
- Which General ledger account the stock value of a material should be managed in or out ?
- How to improve cost of material accuracy ( ie. Landing cost of the material and effective material consumption)
What is Valuation Structure?
The ideas behind the Valuation Structure aid the organization in better valuing their inventory and growing their business.
The list of valuation structrue in SAP.
- Valuation area
- Valuation class
- Valuation category
- Valuation type
- Material type
- Movement type
Valuation Area
The SAP valuation area is basically where materials are valued within an organization. It could be at different levels like the plant or company code level.
So when you set the valuation area at the plant level, you have the flexibility to assign different prices to the same material in different plants.
So, basically, when we talk about valuation at the company code level, it means that the price of a material is consistent across all the plants within that company code.
- Valuation area = company code level ( Common price across company code )
- Valuation area = Plant level ( Common material but different price at plant level )
Valuation Class
A valuation class is a group of materials that have the same account determination. So basically, we can put materials that have similar properties into groups based on their value class.
The valuation class to which a material can be assigned depends on the material type ( Raw Material, Semi-finished,finished )
SAP Valuation Class Rule
- All materials of a material type are assigned to exactly one valuation class.
- Different materials of a material type are assigned to different valuation classes.
- Materials of different material types are assigned to a valuation class.
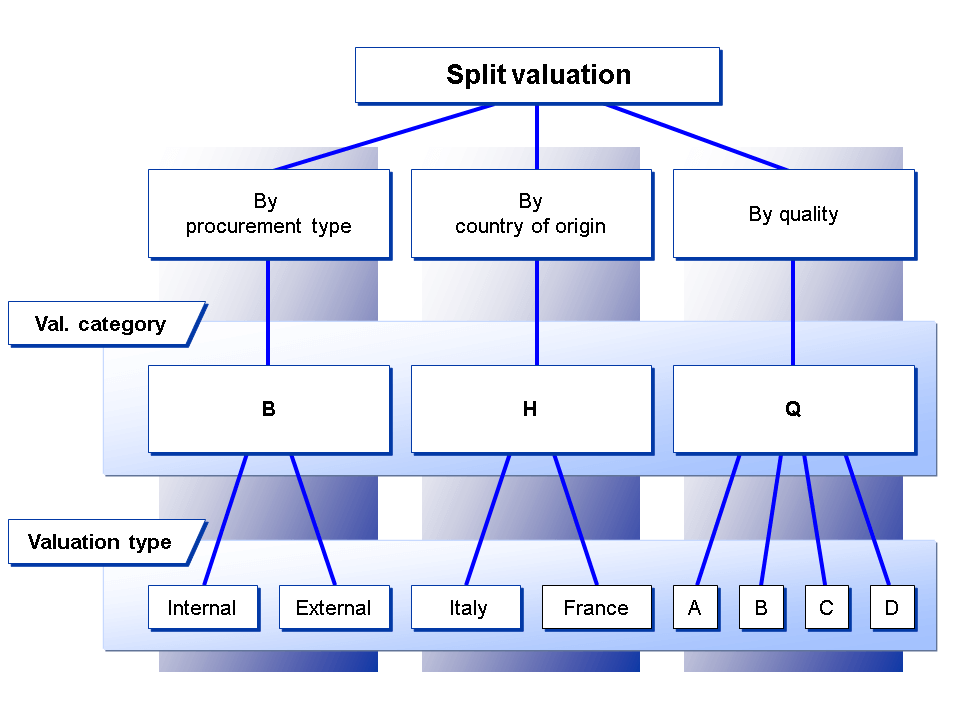
Valuation Category
When it comes to split valuation, each material is assigned to a specific valuation category. So, you can manage the material by using the valuation types that are defined for this valuation category.Valuation category according to which the material is to be valuated.
The system lets you evaluate stocks of a material either together or separately, based on different valuation criteria like Procurement, Origin & Status .
- Procurement: In-house or externally purchased materials are valued differently.
- Origin: Material origin (domestic, import or country specific) can then be used to value it or The value of stock from one manufacturer is different from the value of stock from another manufacturer.
- Status: Materials might be valued differently based on their status (new, used, repaired ( failure rebulid )).
Valuation Type
Each valuation category is associated with specific valuation types that define the particular qualities present within that category. Assigning relevant keys to valuation types allows each valuation type to serve as a representative identifier for a specific sub-stock.
Reference : credit to sap.com.
Example 1:
You procure a material both from in-house production and from external vendors. You want to valuate the stocks from each source separately. In this case, you select Procurement type as the valuation category ( B ) and Internal and External as valuation types.
Example 2:
You procure a material from several countries. You want to valuate the stocks from each country separately. In this case, you select Origin as the valuation category ( H ). As valuation types, you define the relevant countries, for example, Italy and France .
Example 3:
You procure a material in different grades. You want to valuate the stocks of each class separately. In this case, you select Quality as the valuation category ( Q ). As valuation types, you could define A , B , C , and D .
Material type
A material type refers to a categorization of materials that share common characteristics, including materials, semi-finished materials, finished materials, or consumable materials. It is imperative to allocate a specific material type to every entry made in the Material Master.
Standard Material Types
- CONT: Kanban Container
- DIEN : Services
- ERSA : Spare Parts
- FERT : Finished Goods
- FHMI : Production resources/ tools
- HALB : Semi Finished goods
- HAWA : Trading goods
- HERS : Manufacturer parts
- HIBE : Operating Supplies
- LEIH : Returnable packaging
- NLAG : Non Stock material
- PIPE : Pipeline Material
- ROH : Raw Materials
- VERP : Packaging material
Movement Type
movement type is an identifier that is used to determine the kind of material movement occurring within the system. It is possible to tell what kind of transaction is being carried out based on the movement type.
At the end of the day, it is important for us to have a solid understanding of the typical inventory movement technique to analyse opening stock, purchase stock, issue stock, and close stock. SAP will assist you in maximizing the detail approach in order to achieve the strategy described above at the movement type approach.