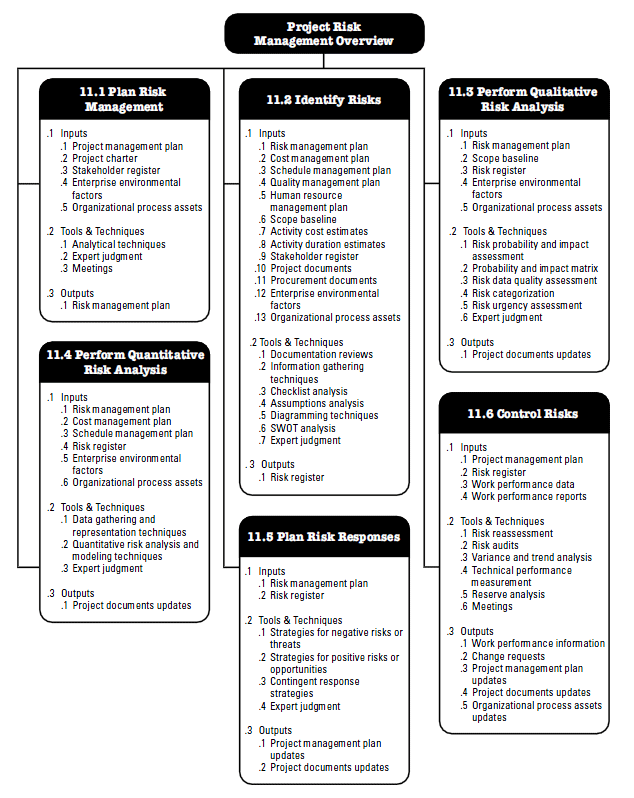
Project risk is an issue that might come up during project management or it could not. While it is impossible to anticipate every risk, planning for it in advance can prevent your project from failing. The impact on the project might be either favorable or unfavorable.
Five Elements of Risk in Project Management
Risk Identification
The process of determining and characterizing risks that could affect a project’s, program’s, or other endeavor’s successful completion is known as risk identification. The goal of this initial phase in risk management is to systematically anticipate, evaluate, and control any negative impact to a business.
Risk Analysis
The next stage is to evaluate each possible risk’s effect and probability after it has been discovered. While effect refers to possible outcomes in the event that the risk materializes, probability refers to the possibility that the risk will occur.
Risk Response Planning
Prioritizing the risks will enable the most important ones to be handled first, based on each one’s effect and likelihood. By doing this, the project’s limited resources are directed on the most significant risks.
Risk Mitigation
To reduce the possible effect of the most significant risks, the project team should create strategies for risk mitigation. Thus, this might entail making adjustments to the project timeline, getting insurance, or creating backup plans.
Risk Monitoring
In conclusion, it is important to consistently review and revise the risk management strategy as the project advances. Maintaining an updated risk management strategy is crucial because new risks might arise and because the probability and consequences of old ones can shift. This guarantees that, over the course of the project, possible risks are mitigated.
Organizations can use a variety of strategies to identify risks.
Brainstorming : Its is a problem-solving strategy used in groups that involves the spontaneous production of innovative ideas and solutions.
Root Cause Analysis : Root cause analysis assists companies in determining the underlying source of an issue, determining suitable corrective measures. and developing a plan to prevent future occurrences. It seeks to implement methods to the underlying problem in order to improve overall project efficiency.
SWOT Analysis : SWOT analysis is a technique for determining and evaluating external opportunities and threats, as well as internal strengths and weaknesses, that influence present and future operations and support in the formulation of strategic project goals.
Risk Identification Template
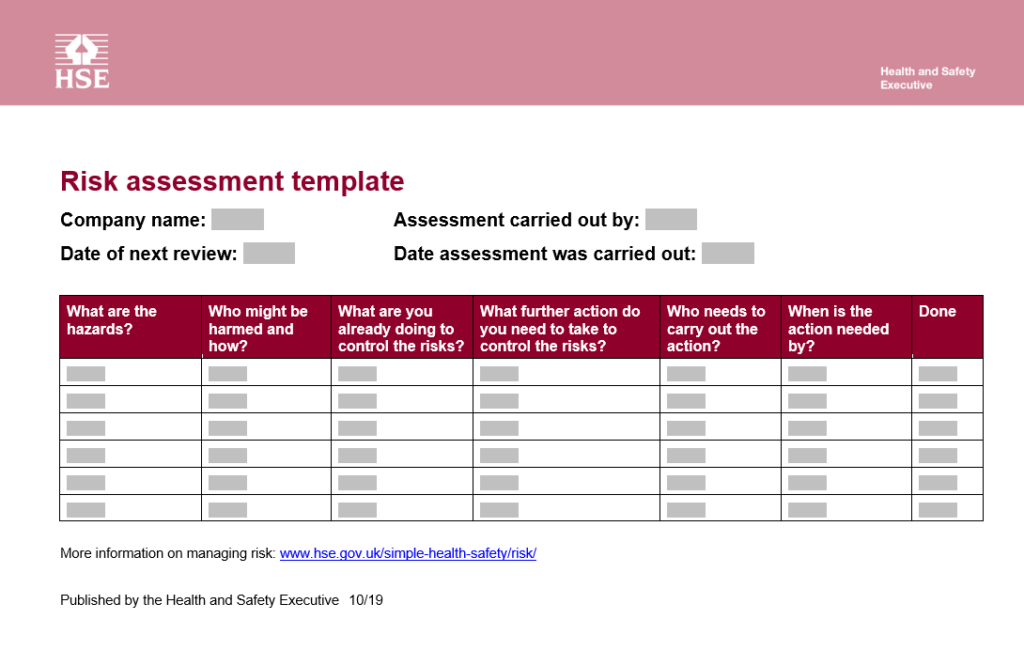
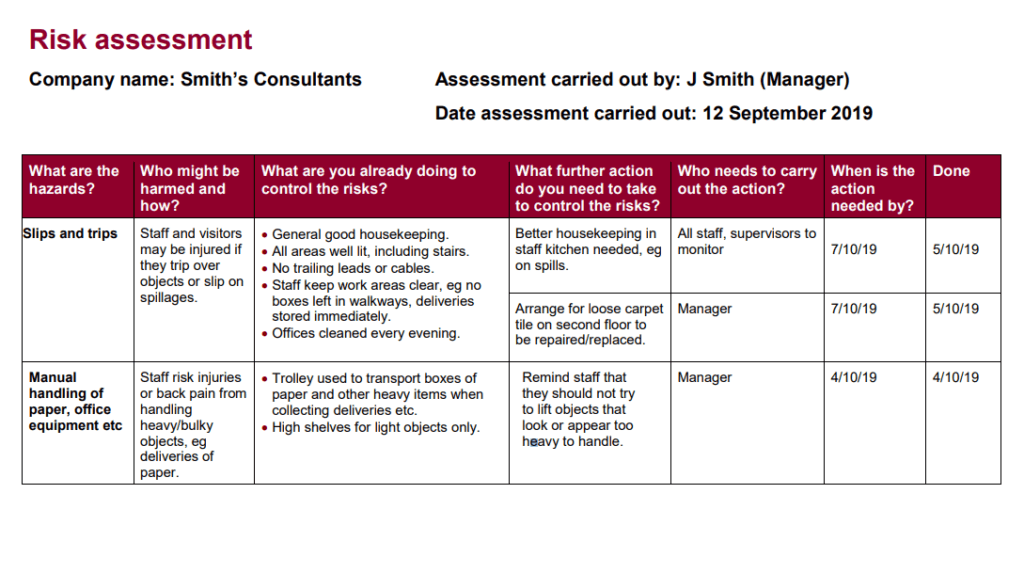
Credit goes to https://www.hse.gov.uk/
Reference and Example : https://www.hse.gov.uk/simple-health-safety/risk/risk-assessment-template-and-examples.htm
Risk Management Strategies
Identifying, evaluating, and reacting to project risks in a proactive manner before they become major problems or affect the project’s completion schedule is known as a risk management method. As part of this procedure, the risk assessment is also periodically updated and reviewed in light of new developments or activities.
Risk avoidance
Risk avoidance reduces the chance of potential risks associated with the project by anticipating them and preparing contingency measures to manage them.
Risk reduction
Implementing a risk reduction plan guarantees that any potential risks are recognized and addressed prior to causing significant problems. The potential that anything will go wrong and undermine the success of your project is reduced when you include this method in your project plan.
Risk transferring
One of the most crucial elements of a successful project is effective risk management. You may lessen the impact of a mishap on the project by transferring the risk to a different entity, shielding it from any consequences or setbacks.
Risk acceptance
By accepting a risk, you admit that there is one and that it may have an effect on the project. This enables you to set up preventative actions and backup plans in case they arise. Accepting risk also frees you up to concentrate more on the advantages of your idea while being ready for unexpected obstacles.
Risk Traffic Light Systems
After the risk assessment is finished, it is frequently beneficial to display the results in a heat map or traffic light system. The following map’s color codes should be understood:
- Red – major or extreme/catastrophic risks that score 15 or more – extra risk management required
- Yellow – moderate or major risks that score between 8 and 14 – regular review and risk management required
- Green – minor or insignificant risks scoring 7 or less – no extra risk management required
X : Probability or Likelihood
Y : Impact or Severity

Risk Management Process
The steps that must be done are outlined in the risk management process.
- Identify the Risk : Risks are now accessible to any stakeholder in the organization
- Analyze the Risk : Risks should be assigned to specific documents, rules, procedures, and business processes.
- Evaluate or Rank the Risk :The risks must be ranked and prioritized ( Qualitative and Quantitative assessments )
- Treat the Risk : Every risk must be reduced or eliminated to the greatest extent possible. Please refer : Risk management Strategies
- Monitor and Review the Risk : Certain risks are always there and cannot be completely eliminated.
PMO BOOK Reference : (PMBOK guide), 1987-1996-2000-2004