Even if you have a brilliant project concept, it won’t become more than an idea without strategy. The crucial first stage in turning an idea into a project’s concrete outcome is planning.
A project plan consists of the following best practice
- Project Charter: Gives a high-level summary of the project. It explains the project’s motivations, goals, objectives, restrictions, and stakeholders, among other things.
- Statement of Work: A statement of work (SOW) describes the scope, timetable, deliverables, milestones, and tasks of a project.
- Work Breakdown Structure: The project scope is divided into project stages, subprojects, deliverables, and work packages that lead to the ultimate delivery.
- Project Plan: The following topics are included in parts of the project plan document: scope management, quality management, risk assessment, resource management, stakeholder management, schedule management, and change management approach.
Project Plan Tempate
Planning Basis : Project Scope, Project Milestones, Project Management Phases, Project Tasks and Resource Requirements
Project Plan : Schedule, Task Dependencies, Project Assumptions and Constraints
Budget, Risk and Change Management Project Budget, Risk Log and Change Management Process
Appendix An appendix is a collection of supplementary materials appearing at the end of a projects
Project milestone examples
Milestones are an important part of project management since they help to keep the project moving forward. Let’s examine five straightforward milestone ideas that you may incorporate into your project plan:
- Start and end dates for project phases
- Key deliverables
- Client and stakeholder approvals
- Important meetings and presentations
- Key dates or outages that may impact your timeline
Monitor deadlines for deliverables, Spotlight important dates and Identify potential project bottlenecks
Work Breakdown Structure /WBS
The Work Breakdown Structure is defined in the Project Management Institute’s (PMI) Project Management Book of Knowledge (PMBOK) as a “deliverable-oriented hierarchical decomposition of the work to be executed by the project team.”
WBSs are classified into two types: deliverable-based and phase-based. The Deliverable-Based method is the most prevalent and recommended strategy. The Elements indicated in the first Level of the WBS are the key distinction between the two methodologies.
Breaking work down into smaller jobs is a typical productivity method intended to make work more manageable and accessible. The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a tool that uses this method for projects and is one of the most significant project management papers. It incorporates scope, cost, and schedule baselines all on its own, ensuring that project plans are in sync.
Terms that are often used in WBS project management include
- Acceptance Criteria: Standards should be fulfilled in order to satisfy demands from customers or other stakeholders
- Budget: Project-related costs, which can be divided into stages or deliverables
- Deliverables: the output—a service, good, or outcome—produced at different project phases. In a deliverable-based work breakdown structure (WBS)
- Milestones:The WBS identifies the project’s critical phases.
- Phases: The several stages of a project.
- WBS: Work breakdown structure
Deliverable-Based Work Breakdown Structure
A Deliverable-Based Work Breakdown Structure effectively displays the link between project deliverables (products, services, or outcomes) and scope (work to be completed).
Phase-Based Work Breakdown Structure
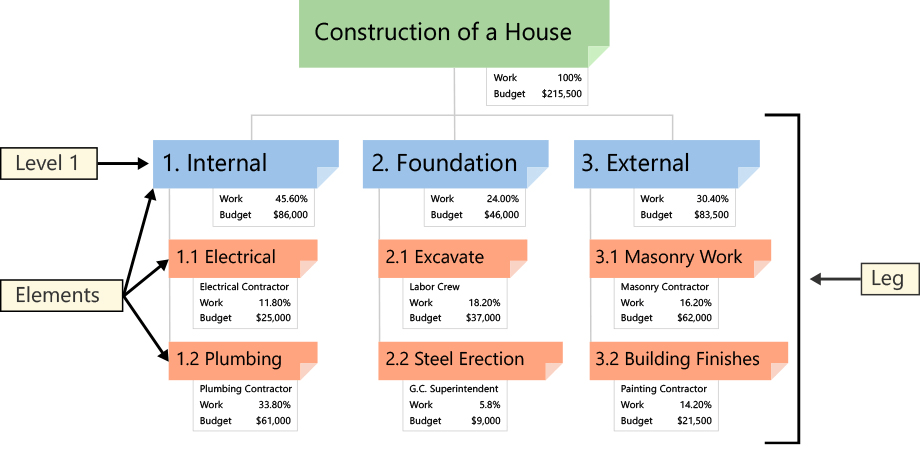
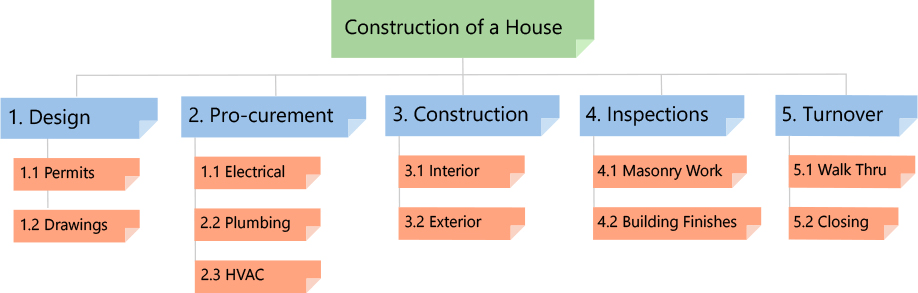
The Level 1 WBS is a Phase-Based WBS with five Elements. Each of these Elements represents a typical project phase. The Level 2 Elements are the phase-specific deliverables. Lower Level Elements are all deliverables, regardless of the kind of WBS. It’s worth noting that Elements in different Legs share the same name. Work associated with numerous components must be split into work specific to each Level 1 Element in a Phase-Based WBS. To explain the work in each Element, a WBS Dictionary is generated.
Construction Of A House
Reference : https://www.workbreakdownstructure.com/
Project Phase and Project Budget in control
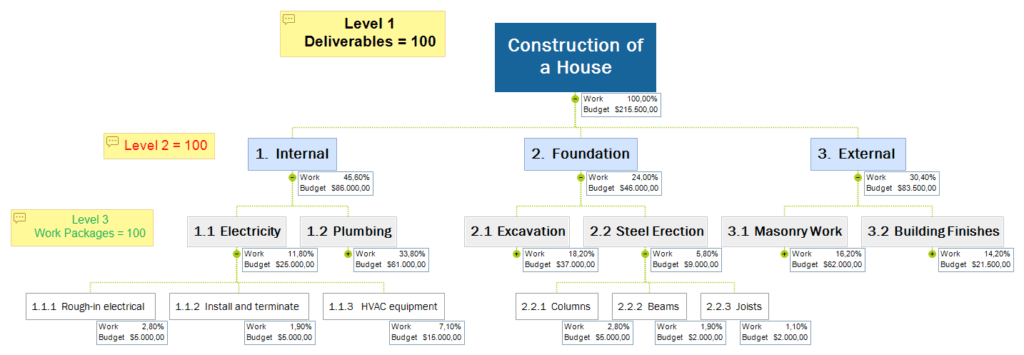
More Example : pelase refer : https://www.workbreakdownstructure.com/work-breakdown-structure-examples
Estimation techniques
Guesstimation : A Guesstimation is an approximate estimate method (guess and estimate) with limited information used for an initial planning.
Guess + Estimate : Guesstimates are approximate estimations, rapid calculations performed in circumstances with little data. This sort of comment might be unnerving at first.
https://www.projectmanagement.com/blog-post/59488/The-Art-of-Guesstimation–Why-Shouldn-t-We-Estimate-: Planning & WBS – Project ManagementDelphi Technique : A method for making complicated decisions by utilizing individual knowledge. This approach is also known as the “Wide-band Delphi” technique. A method for estimating the probability and outcome of future occurrences.
https://www.projectmanagement.com/wikis/233600/Delphi-Technique: Planning & WBS – Project ManagementSteps of the Delphi Technique
- Choose a Facilitator
- Identify your Experts
- Define the problem and research question
- Carry out three response ( i.e Three rounds) and feedback rounds ( i.e Three rounds)
- Act on your Findings




