Microsoft Defender for Cloud is a workload protection and security posture management solution that is compatible with Azure and hybrid cloud environments.
Azure, on-premises, and multicloud (Amazon AWS and Google GCP)
Secure score, Security recommendations, security alerts, advanced protection capabilities, Vulnerability assessment and management
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
Automates cloud security management across the following diverse infrastructure: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS), and Platform as a Service (PaaS). Automates cloud risk identification and remediation.
Cloud Workload Protection (CWP)
Cloud Workload Protection (CWP) continuously monitors and removes threats from cloud workloads and containers. A Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP) provides unified cloud workload protection across multiple providers for all types of workloads.
Provide comprehensive defenses for the Servers, App Service, Storage, Databases, Containers, Key Vault, Resource Manager, DNS and more
Azure Arc’s unified multi-cloud and on-premises management platform simplify governance and management.
Defender for Cloud meets three critical security demands for cloud and on-premises resources and workloads
- Continuously Assess – Understand your current security posture.
- Secure – Harden all connected resources and services.
- Defend – Detect and resolve threats to those resources and services.
Azure: Defender for Cloud’s security policy is reflected in Azure Policy as a built-in initiative under the Defender for Cloud category when enabled.
The built-in initiative is automatically assigned to all Defender for Cloud registered subscriptions.
The built-in initiative contains only Audit policies
The native Azure connection (including Azure Policy, Azure Monitor logs, and Azure resources ) and seamless connectivity with other Microsoft security solutions like Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint assist make your security solution comprehensive and easy to onboard and roll out.
Protection for cloud resources in Microsoft Defender can be set up either automatically through auto-provisioning or manually.
Network map
The Network map is Defender for Cloud’s most effective tool for monitoring network security. You may check each node’s configuration by seeing your workload topology on the map. You can see how your nodes are connected, which helps you block unwanted connections that could allow an attacker to sneak through your network.
Recommended controls
By identifying vulnerabilities and outlining remediation steps, Defender for Cloud relieves you of the burden of being a security administrator.
All of your resources, including Azure VMs, non-Azure servers, and Azure PaaS services like SQL and Storage accounts, can benefit from the recommendations made. The value of various resources is calculated using their respective sets of standards.
Threat protection
Fusion kill-chain analysis in Defender for Cloud automatically correlates environment warnings based on cyber kill-chain analysis. The research highlights an attack campaign’s origins and resource impact.
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
Defender for Cloud includes automatic, native integration with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
Defender for Cloud’s adaptive application controls enables Windows server-wide app approval listing. You don’t have to write and enforce rules.
Platform as a Service Defender for Cloud helps you identify threats across Azure PaaS services.
Block brute force attacks
Defender for Cloud reduces brute-force assaults. Just-in-time VM access reduces unwanted virtual machine port access, hardening your network. Secure access policies on chosen ports can be defined for approved users, allowed source IP address ranges or IP addresses, and a limited time.
Asset inventory
The Azure Resource Graph (ARG) is used for the inventory of assets. This Azure service provides access to the security posture data of all Defender for Cloud subscriptions and can be queried by the user. ARG is made to allow for large-scale querying and effective exploration of resources. In order to query data, ARG uses the Kusto language (KQL). By comparing ASC data with other features of assets, an inventory can quickly generate in-depth insights.
Auto-provisioning
When auto-provisioning is enabled, the Azure Security Center installs the Microsoft Monitoring Agent (MMA) on all supported Azure VMs, including new ones. Azure Security Center collects security-related parameters and event logs from your virtual machines and transmits the data, including crash dump files, to your workspace for investigation when the MMA is installed. Missing updates, incorrect OS security settings, endpoint protection settings, and health and threat detections must be visible in the data submitted for analysis.
Event types
Minimal: successful breaches and important events that have a low volume.
Common: Provide a full user audit trail in this set
Non-Azure Connection
Defender for Cloud secures non-Azure servers and virtual machines in the cloud or on-premises by installing the Log Analytics agent on them.
Azure Arc-enabled servers enable guest configuration policies, deploy the Log Analytics agent as an extension, simplify deployment with other Azure services, and more.
The Azure Connected Machine agent must be installed on all hybrid machines hosted outside of Azure to enable this experience. It does not replace the Azure Log Analytics agent. When monitoring the OS and workloads on a Windows or Linux machine, you need the Log Analytics agent.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Microsoft Defender for Cloud connects AWS account with AWS Security Hub.
- Enable AWS Config.
- Enable AWS Security Hub.
- Verify that there’s data flowing to the Security Hub.
There are two ways to allow Defender for Cloud to authenticate to AWS
- Create an IAM role for Defender for Cloud – This is the most secure method and is recommended.
- AWS user for Defender for Cloud – A less secure option if you don’t have IAM enabled.
Google Cloud Platform Services(GCP)
Microsoft Defender for Cloud connects GCP account with GCP Security Command Center.
- Set up GCP Security Command Center using these instructions from the GCP documentation.
- Enable Security Health Analytics using these instructions from the GCP documentation.
- Verify that there’s data flowing to the Security Command Center.
Security Policy
Mainly, Defender for Cloud relies on policies labeled “Audit,” which examine granular conditions and settings and then report on whether or not they are compliant. The “Enforce” policy can also be used to implement security measures.
Security Initiative
Security initiatives help you meet company and regulatory security standards by defining your workload configuration.
View and edit the built-in default initiative, Add your own custom initiatives, and add regulatory compliance standards as initiatives.
Security Recommendation
Based on your initiatives, Defender for Cloud recommends security. Defender for Cloud makes a recommendation when your initiative’s policy is compared to your resources and detects non-compliant ones.
Secure Score
To improve security, check Defender for Cloud’s recommendations page and follow the steps for each issue. Recommendations are security controls. Each control is a logical group of connected security recommendations and represents your vulnerable attack surfaces
Remediating all resource recommendations within a control raises your score.
Recommendations
Defender for Cloud uses Azure Security Benchmark recommendations. Microsoft’s Azure Security Benchmark provides security and compliance best practices based on common compliance frameworks. This well-respected benchmark focuses on cloud-centric security and builds on CIS and NIST regulations. Regulator compliance initiatives produce other suggestions.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud monitors your resource configuration against industry standards, laws, and benchmarks. The regulatory compliance dashboard shows how you’re meeting compliance standards.
Each standard is an initiative defined in Azure Policy.
Workbooks
Azure Monitor Workbooks offer a flexible canvas for doing in-depth data analysis and developing visually stunning reports. They make it possible to access disparate data stores in Azure and merge them into a single interactive experience.
Workbooks readymade
- Secure Score Over Time workbook – Track your subscriptions’ scores and changes to recommendations for your resources
- System Updates workbook – View missing system updates by resources, OS, severity, and more
- Vulnerability Assessment Findings workbook – View the findings of vulnerability scans of your Azure resources
- Compliance Over Time workbook – View the status of a subscription’s compliance with the regulatory or industry standards you’ve selected
- Active Alerts workbook – view active alerts by severity, type, tag, MITRE ATT&CK tactics, and location.
Workload Protections
Microsoft Defender for servers
- Integrated license for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint: Endpoint detection and response (EDR) capabilities
- Vulnerability assessment tools for machines: discovered vulnerabilities are shown in a security recommendation
- Microsoft threat and vulnerability management: Microsoft Defender for Endpoint detects vulnerabilities and misconfigurations without agents or periodic scans.
- Vulnerability scanner powered by Qualys: Qualys is a leading solution for real-time vulnerability detection in Azure and hybrid virtual machines.
- Just-in-time (JIT) virtual machine (VM) access: Just-in-time VM access lets you restrict VM inbound traffic using Microsoft Defender for Servers. Keeping remote access ports closed until needed reduces assaults and makes connecting to VMs straightforward.
- File integrity monitoring (FIM): change monitoring checks the operating system, application, and other files and registries for attacks. The file’s current status is compared to its last scan. This comparison might help you identify unusual file changes.
- Adaptive application controls (AAC): If any app other than your secure ones runs, you get security alerts.
- Adaptive network hardening (ANH): Adaptive network hardening suggests NSG rule hardening. A machine learning algorithm considers actual traffic, trusted configuration, threat intelligence, and other indicators of compromise. ANH then recommends allowing only particular IP and port tuples.
- Docker host hardening: Defender for Cloud warns you if your containers violate any CIS Docker Benchmark restrictions.
- Fileless attack detection: Fileless attacks hide harmful payloads in memory to bypass disk-based scanning. The attacker’s payload stays in compromised processes’ memory and executes a range of malicious activities.
- Linux auditd alerts and Log Analytics agent integration (Linux only): Defender for Cloud combines auditd functionality into Log Analytics. This integration collects auditd events in all supported Linux distributions without requirements.
- Linux Log Analytics agent enriches and aggregates auditd records into events. Defender for Cloud continuously adds Linux signal analytics to detect malicious activities on cloud and on-premises Linux servers. This analytics monitor for suspicious processes, sign-in attempts, kernel module loading, and other activities like Windows. These behaviors may suggest a breached or attacked machine.
Microsoft Defender for Storage
Microsoft Defender for Storage is an Azure-native security intelligence layer that detects suspicious and potentially unsafe storage account access attempts. Security AI and Microsoft Threat Intelligence give contextual security alerts and recommendations.
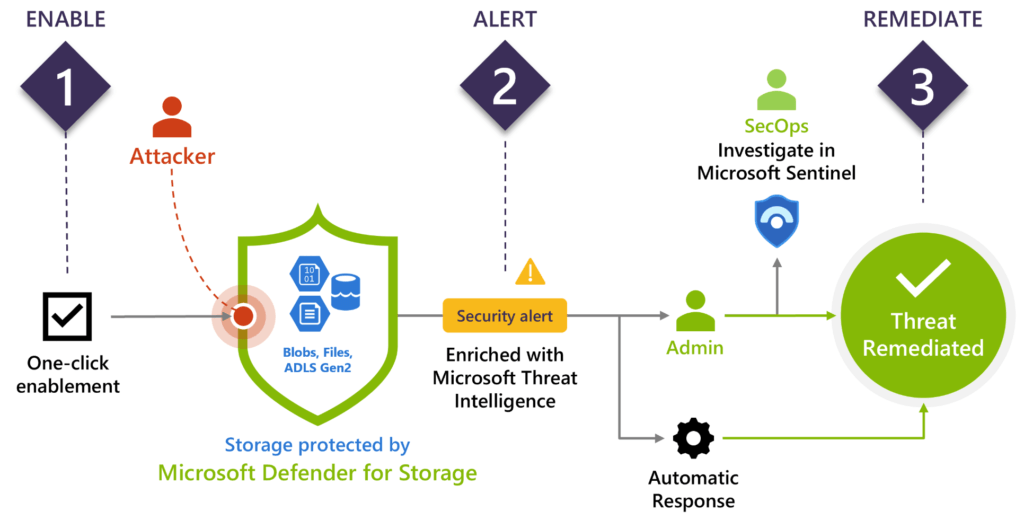
Suspicious access patterns Tor exit node or suspicious IP
Suspicious activities anomalous data extraction or access permission changes
Uploads of malicious content malware (based on hash reputation analysis) or phishing content.
Threats can be identified through reputation analysis by looking for suspicious domain names, IP addresses, and file hashes that are known to be associated with malicious behavior.
Defender for Storage employs Microsoft Threat Intelligence-supported hash reputation analysis to identify suspicious files. Threat protection doesn’t scan submitted files. Instead, they check storage logs and compare newly uploaded file hashes to known viruses, trojans, malware, and ransomware.
Microsoft Defender for SQL
- Potential SQL injection attacks -improper SQL statements in the database.
- Anomalous database access and query patterns -a significant number of failed login attempts with different credentials (a brute force attempt)
- Suspicious database activity – For instance, a genuine user accessing a SQL Server from a hacked PC that connected with a crypto-mining C&C server.
Open-source relational databases
- Anomalous database access and query patterns a significant number of failed login attempts with different credentials (a brute force attempt)
- Suspicious database activities For instance, a genuine user accessing a SQL Server from a hacked PC that connected with a crypto-mining C&C server.
- Brute-force attacks Ability to distinguish between a simple brute force attack and one that targets a valid user or is successful in its brute force attempt.
Microsoft Defender for Azure Cosmos DB
- Potential SQL injection attacks: Azure Cosmos DB queries are too structured and powerful for many SQL injection attacks. SQL injections can exfiltrate data from Azure Cosmos DB accounts, but not all of them.
- Anomalous database access patterns: TOR exit nodes, suspicious IP addresses, unusual apps, and unusual locations.
- Suspicious database activity: Suspicious data extraction and key-listing patterns that mirror known malicious lateral movement strategies.
Microsoft Defender for Key Vault
Microsoft Defender for Key Vault detects suspicious activity caused by stolen credentials. If you recognize the user or application, don’t dismiss the alert. Contact the application owner or user to confirm the activity. If necessary, create a suppression rule to eliminate noise.
- Unrecognized IP address traffic Enable the Azure Key Vault firewall Firewalls and virtual networks for Azure Key Vault. Set up the firewall with trusted resources and virtual networks.
- Unauthorized application or suspicious user Open the key vault’s access policy. Remove the security principal or limit its operations.
- Azure Active Directory role in your tenant Contact the administrator. Check if Azure Active Directory permissions should be reduced or revoked.
Microsoft Defender for Resource Manager
It provides a management layer for creating, updating, and deleting Azure resources. After deployment, you use management tools such as access control, locks, and tags to secure and organize your resources.
- Suspicious resource management operations, such as suspicious IP addresses, disabling antimalware, and suspicious scripts in VM extensions.
- Use of exploitation toolkits like Microburst or PowerZure
- Lateral movement from the Azure management layer to the Azure resources data plane
Microsoft Defender for DNS
Azure DNS is a hosting service for DNS domains that use Microsoft Azure infrastructure to provide name resolution.
- Data exfiltration from your Azure resources using DNS tunneling
- Malware communicating with the command-and-control (C&C) server
- Communication with malicious domains such as phishing and crypto mining
- DNS attacks – communication with malicious DNS resolvers
Microsoft Defender for Containers
- Environment Hardening Defender for Containers enables continuous assessment of clusters, revealing misconfigurations and offering guidelines to assist mitigate threats.
- Vulnerability Assessment Vulnerability evaluation and management tools for ACR-registries images operating in Azure Kubernetes Service.
- Run-time threat protection for nodes and clusters Threat protection for clusters and Linux nodes alert for unusual activity. “MITRE ATT&CK® matrix for Containers”
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), An unmanaged Kubernetes distribution (using Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes
Threat protection: Azure network layer, Azure Cosmos DB (Preview), Azure WAF alerts, Azure DDoS Protection, Cloud Apps