Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services over the internet.
The usage of hosted services, such as data storage, servers, databases, networking, applications, services, software Internet of Things (IoT), machine learning (ML), and artificial intelligence (AI), through the Internet is known as “cloud computing.” The data is kept on actual servers that a cloud service provider manages.
Types of Cloud Computing
You may categorize cloud computing either depending on the deployment model or the kind of service.
Typically, deployment models categorize clouds as public, private, or hybrid, another new model is Multi-cloud depending on the type of deployment choice made due to business demands.
In accordance with the services that the cloud model provides, service models are categorized as infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), platform-as-a-service (PaaS), and software-as-a-service (SaaS).
In contrast to traditional datacenters, cloud computing is not restricted by physical infrastructure because it leverages the internet to deliver these services. You can use the cloud to quickly extend your IT footprint if you need to enlarge your IT infrastructure but don’t want to wait to build a new datacenter.
Private cloud: A private cloud represents a company’s data center and is managed by you. Simply traditional infrastructure
Public cloud: Name itself elaborating on the characteristics of clouds. A third-party cloud provider creates, manages, and maintains a public cloud.
Hybrid cloud: ( Private + Public Cloud): A hybrid cloud is a computer platform that utilizes both public and private clouds in a networked environment.
Multi-cloud: In a multi-cloud setup, you manage resources and security across two or more public cloud service providers.
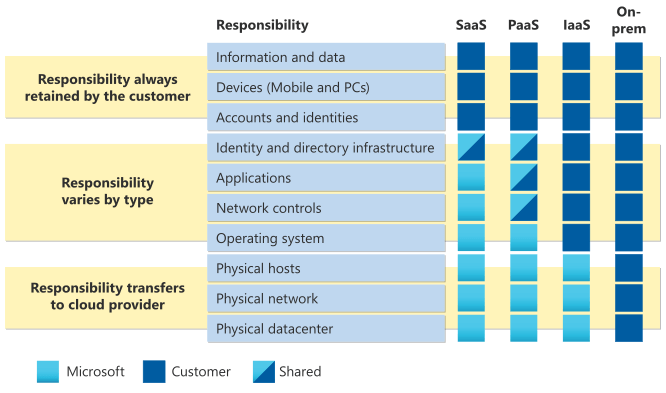
Cloud Services: Depending on the kind of cloud service, the shared responsibility model specifies who is in charge of what.
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS): In this model, the service provider stores and manages the infrastructure and then makes it available to consumers on demand. Provides on-demand access to computing, storage, and networking resources in the cloud.
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS): full-fledged cloud-based setting for creating, deploying, and maintaining software applications, including all the necessary tools and infrastructure.
Software as a service (SaaS): Software distribution models that allow end-users to access and utilize cloud-based applications via an online connection and pay for such services on an ongoing subscription basis are what we call “software as a service.”