Data backup is the process of copying data to retrieve it from a copy set if the original data is lost. The Azure Backup service makes it easy, safe, and cost-effective to back up your data and get it back from the Microsoft Azure cloud.
Encryption protects your cloud data. The encryption passphrase is saved locally and never sent to Azure. If you need to restore any of the data, only you have the encryption passcode or key not azure.
With Azure Backup, you can choose between two different replication strategies, both of which will keep your data and storage systems highly available at all times.
Locally redundant storage ( LRS): within the same region, three copies of your data are present.
Geo-redundant storage (GRS): GRS replicates your data to a secondary region even during a regional outage.
List of backup solutions
- On-premises: Microsoft Azure Recovery Services (MARS) agent (Linux machines aren’t supported ) or Azure Backup Server (MABS) agent or System Center Data Protection Manager (DPM) sends data into the “Recovery Services vault in Azure”.
- Azure VMs: Back up entire Windows/Linux VMs – A backup extension to the Azure VM agent and MARS agent to access Azure VM files and directories
- Azure Managed Disks: Backup vault and backup policy
- Azure Files shares: Azure file share backup is a native, cloud-based backup solution
- SQL Server in Azure VMs: Back up SQL Server databases running on Azure VMs
- SAP HANA databases in Azure VMs: Backup SAP HANA databases running on Azure VMs
- Azure Database for PostgreSQL servers: Back up Azure PostgreSQL databases and retain the backups for up to 10 years
- Azure Blobs: operation backup Blobs, a controlled, local data security system, protects block blobs from corruptions, blob deletions, and inadvertent storage account deletion.
The Recovery Services vault is a storage entity in Azure that stores data. Recovery Services vaults for short-term and long-term data retention. Azure Backup has a 9999 recovery point limit per protected instance.
Azure subscriptions allow 500 Recovery Services vaults per region.
Azure VM extension: Runs on Azure VMs to back them up to a vault.
You may use Recovery Services vaults to store backup data for a wide variety of Azure services, including IaaS VMs (whether they’re running Linux or Windows) and SQL Server in Azure VMs. The vaults offered by Recovery Services are compatible with System Center DPM, Windows Server, the Azure Backup Server, and more.
With soft delete, data is not lost if a backup is unintentionally or maliciously destroyed; instead, it is kept for 14 days so that it can be restored. You won’t be charged anything more for the backup data’s extra 14 days in the “soft delete” condition.
Soft delete only protects deleted backup data. If a VM is deleted without a backup, the soft-delete feature won’t preserve the data
Azure Backup offers three types of replication :
- Locally redundant storage (LRS) : Replicates your data three times with in same region .
- Geo-redundant storage (GRS) : Replicates your data to a secondary region (hundreds of miles away from the primary location of the source data).
- Zone-redundant storage (ZRS) : Replicates your data in availability zones, guaranteeing data residency and resiliency in the same region.
General Backup Types
- Full: Used for the initial backup.
- Differential: Not used by Azure Backup.
- Incremental: Used by DPM (Data Protection Manager )/MABS for disk backups, and used in all backups to Azure. Not used for SQL Server backup.
SQL Server backup types
- Full backup: Full database backups include everything. It holds all data in a database or filegroup. Full backups have enough logs to restore data.
- Differential backup: Full and differential backups cannot be configured on the same day.
- Transaction log backup: Log backups allow second-by-second restoration.
SAP HANA backup types
Full backup: Backup can separately restore to a certain point.
Differential backup: Differential backups use the most recent full-data backup. Full and differential backups cannot be configured on the same day.
Incremental backup: A database can only have one delta backup type, not both differential and incremental.
Transaction log backup: Log backups allow second-by-second restoration.
Azure Backup Center
In order to administer, monitor, run, and analyze backups at scale, businesses can use Backup Center, a unified management experience in Azure.
Backup Center manages backups using Azure Policy. Azure Workbooks and Azure Monitor Logs provide backup reports.
It also gives Azure Site Recovery the ability to be monitored and managed at a large scale.
Azure VM backup, SQL in Azure VM backup, SAP HANA in Azure VM backup, Azure Files backup, Azure Blobs backup, Azure-managed disks backup, and Azure Database for PostgreSQL Server backup
Currently Supported resource
Backup Policy
Each vault has a backup policy. A backup policy is created per vault.
A policy has two components:
Schedule: When to take the backup
Retention: For how long each backup should be retained.
Azure Virtual Machine Backup
- Azure Backup: Backups for both Windows and Linux VMs. Can restore the whole VM or just specific files or folders from the backup.
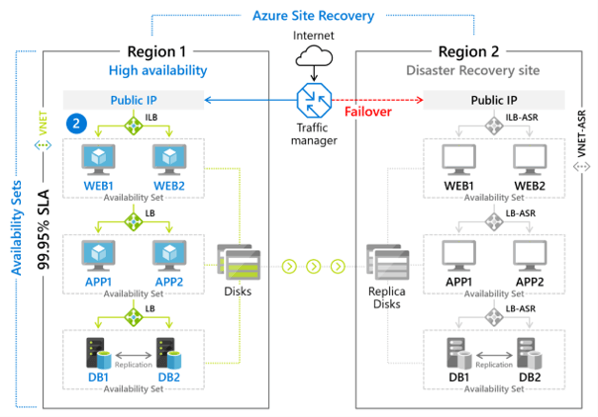
- Azure Site Recovery is used when a major natural disaster or service interruption strikes an Azure region.
- Managed disk snapshots: full read-only copy of a managed disk that is stored as a standard managed disk by default.
- Images: Captures a single image, and its contains all managed disks associated with a VM, including both the OS and data disks
- Images versus snapshots: A snapshot is a copy of a disk at the time the snapshot is taken. It applies only to one disk but the image includes all of the disks attached to the VM.
Start with a virtual machine snapshot. Second the virtual machine snapshot is then moved to Azure Recovery Services.
- After the snapshot, the recovery point is generated but only after both steps are completed
- You can do a restore from this recovery point.
- When a snapshot is moved to the vault, the type of recovery point changes to “snapshot and vault.”
Characteristics
- Ability to recover backup snapshots without waiting for data transfer to the vault.
- Reduces backup and restore times by keeping snapshots locally for two days by default but the default snapshot retention value can be set to 1–5 days only.
- Azure Backup doesn’t recommend disc resizing and supports disk sizes up to 32 TB also Supports HDD, SSD, and Premium SSD drives.
- Incremental snapshots are stored as page blobs and Instant recovery point snapshots contribute toward the 10-TB limit for premium storage accounts.
- Snapshot retention to one day in the backup policy blade. If you don’t restore often, this will save snapshot retention costs.
Azure Site Recovery
Replicates data from one location to another. If your primary site goes down, you go to the secondary site and use applications there. You can return to the primary location once it’s functioning.