Short-term debt and a liability on the balance sheet, accounts payable (AP) represents a company’s obligation to pay for products and services that it has received on credit from its suppliers. ( vendors )
Accounting records show that customers who bought goods or services on credit owe money to the business. This is called accounts receivable (AR) in the general ledger (GL).
Business Partners
A business partner is a person or organization in which your company has a business interest
Each new business partner is allocated to one of three categories
Persons
A natural person is a private individual and consists of person-related data, for example date of birth, martial status, private address, etc.
Organizations
Legal entity or part of a legal entity, for example, company, department in a company, club, or association.
Groups
A Business partner group is a group of natural persons or a group of organizations, that is, a purchasing community or a shared living arrangement. A group specifies a joint practice, joint proprietaries, a household, a married couple, or an executive board, etc.
Business Partner Roles
Rights and responsibilities that a business partner (BP) may be expected to take on as part of a variety of different business transactions
Role Grouping
By utilizing role grouping, you may declare which roles are maintained simultaneously. Using this as a task aid speeds up master data generation. This implies that a single person or department can accurately keep all important data fields.
To ensure consistent data management, companies may group roles to maintain customers for both SD and FI, or suppliers for SAP ERP Materials Management (MM) and Fl. Centralized maintenance ensures preparedness for business partners when data is stored.
BP Number Range
Number ranges for BPs are valid throughout a client of a particular system . The Number range and grouping allow you to classifiy the customer and vendor faster and effectively.
Customer and Supplier Account Groups
Create and manage account groupings for customers and suppliers in the FI component. These categories categorize consumers and suppliers by region, size, or association. For instance, distinct account groups are typically created for domestic and overseas customers/suppliers.
One-Time Accounts and Normal Accounts
One-time accounts (OTAs) are a unique subset of customer or vendor master data. Until the time the document is actually produced in the system, one-time accounts do not record any information about the client or supplier. When creating an invoice, you’ll be able to include your contact information, tax information, and financial information.
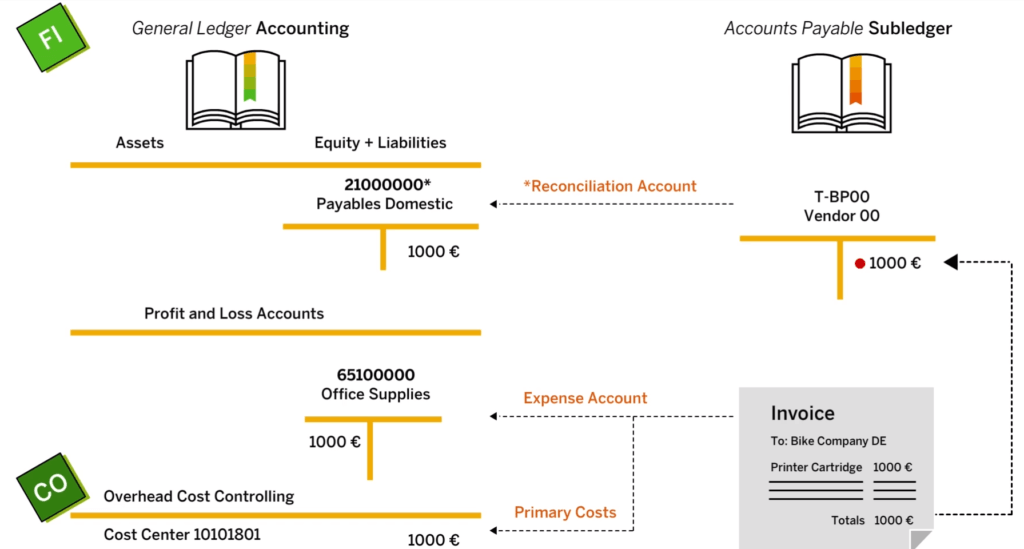
Reconciliation Account
When making a transaction in either the customer or supplier ledger, the transaction should be sent to this reconciliation account. The reconciliation account is a general ledger (G/L) account that can only receive postings from other G/L accounts (customers and suppliers).
Payment Terms
The computation of the due date and the discount are both determined by SAP based on the terms of payment. The terms of payment are set to default at the invoice level in both the vendor master and the customer master databases; however, these settings may also be altered at the invoice level.
Payment Methods
The payment method specifies the procedure, such as check, transfer or bill of exchange, by which payments are made.
The following payment methods are usual in Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable:
| Accounts payable | Accounts receivable |
|---|---|
| Check | Bank collection |
| Transfer | Bank Direct Debit |
| Postal giro transfer | Refund by check |
| Bills of Exchange | Refund by bank transfer |
| Check/bill of exchange | Bank billsBill of exchange payment request |
Tolerance Group
Tolerance Groups contain the details that control the way the system processes the cash discount and payment differences..
Posting Block/Payment Block
Posting block restrictions prevent the dissemination of any document to the business associate. By implementing payment blocks, only payments are impeded.
House Bank
This bank is the default account through which payments are made or received.
Individual Payment
The system generates a distinct payment document for each invoice when individual payments are selected.
Clearing with Customer
This enables the clearance process between suppliers and customers (when a supplier is associated with a customer and vice versa).
Correspondence
The term “accounts correspondence” can also be used to describe the written record of company conversations and the ensuing interactions with suppliers and clients.
Exampe : Payment notices, Customer statements, vendor statements, closing write-off etc..
Withholding Tax
For services from international suppliers or individuals, an organization deducts withholding tax. A party or entity deducts tax while paying the provider. The withheld tax rate or amount is set by the appropriate tax regulations in each nation and should be submitted to the tax authorities within the specified timeframe.
Manual Payments
Outgoing payments must be communicated to the bank via the system. Most banks get this via electronic data exchange for direct debits and wire transfers or an electronic payment file for bank transfers. The bank receives payment information via payment forms.
Nevertheless, the system is also able to generate outgoing payments even if the payment forms that are established in the system are not used. The manual payment forms are utilized in the creation of these payments.
Example based on Invoice and financial posting.
Automatic Payments
The SAP S/4HANA Automatic Payment Program (APP) handles large outgoing and receiving payments. It may be customized to meet the demands of every country’s implementation. Making local, foreign, and intercompany payments, clearing open items between customers and suppliers, and more are possible.
Payment medium
The payment medium format refers to the specific structure of the output data media used in Data Media Exchange (DME) for payment transactions.
Payment Medium Workbench
The Payment Medium Workbench is a platform that allows for the definition and creation of DME forms. These might be utilized right away throughout the process of running the payments. The Data Medium Exchange Engine (also known as DMEE) is often where the formats are defined.
SAP provides a wide variety of universally accepted payment types for countries. These may be copied and modified in Customizing using the DMEE tool.
Expenses/Charges
When recording incoming and outgoing payments, bank charges might be included to account for any fees associated with the payments received or made.
Dunning – Payment due reminders
When a customer (or occasionally a supplier with a debit balance) has an open item that is past due, the dunning procedure is used to “remind” them to pay the bill. The late payment penalty and the severity of the reminders can be escalated over time. The dunning configuration and execution apps in SAP S/4HANA allow you to automate the dunning process based on business rules.
Dunning Areas
If multiple divisions within an organization are responsible for dunning under a single business policy, then you should set up dunning areas. In the SAP system, these divisions are known as dunning areas.
Example : Goods Retail, Whole sales, Services Zone and etc…
Dunning Keys
Dunning keys enable you to limit the dunning level for an item. They also allow you to control whether the items with dunning keys are to be displayed separately in the dunning notice
Dunning Blocks
Dunning blocks enable you to prevent an account or an item from being dunned. Enter a blocking key in the field Dunning block in the master record or in the item.
Example : Promised to pay with X days, dispute raised, waiting for management feedback to take action.
Dunning Procedures
The dunning program duns open items in customer and vendor accounts if the overdue items result in a debit balance. When you configure the dunning program, you can specify additional criteria for determining whether accounts or their open items are to be dunned.
The dunning frequency and/or the dunning interval with which accounts are dunned.
Special General Ledger Accounting
Special G/L transactions are special transactions in accounts receivable and accounts payable that are displayed separately in the general ledger and the subledger. This is achieved by posting to alternative reconciliation accounts, instead of posting to the reconciliation accounts for receivables and payables.
Reference : sap.com
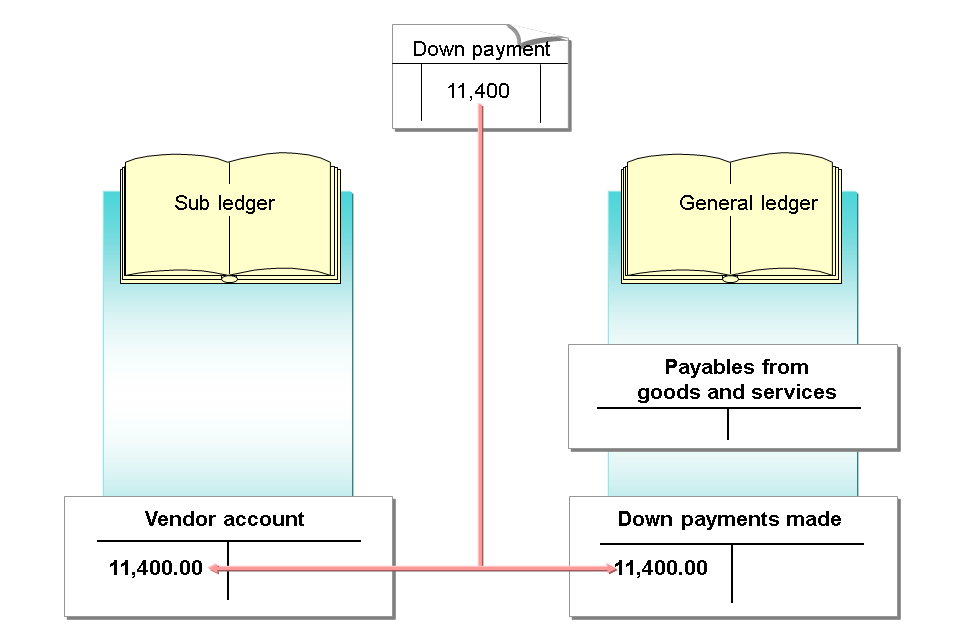
The following special G/L transactions are available:
- Down payments and down payment requests
- Bills of exchange receivable, bills of exchange payable and checks/bills of exchange
- Bank bills
- Payment requests
- Guarantees
- Reserves for bad debt
- Security deposits
These special procedures are displayed separately from other receivables and payables on the balance sheet either for legal reasons, such as with down payments, or for control reasons, such as with guarantees received. A separate special G/L account is created for each special G/L transaction. As a result, it is possible to display each transaction in the balance sheet without having to carry out any transfer postings and to receive an overview via the account limited to this procedure only.